The Big Crypto Cheat Sheet: Everything You Need to Know to Win With Digital Currencies

What’s So Special About Bitcoin?
What Was the “Bitcoin Halvening”?
Which Crypto Has the Most Potential?
Why Are Blockchains Important?
Why Do Some Crypto Exchanges Not Operate in Certain States?
What Are My Crypto Wallet Options?
Do I Have to Pay Taxes on My Crypto Returns?
What Are the Risks Involved in Buying and Selling Crypto?
Why Are Some Cryptos So Volatile?
I’m Ready to Get Started With Crypto! What Now?
What Is Cryptocurrency?
In the simplest terms, a cryptocurrency (crypto) is a digital asset that can be bought, sold or exchanged via a decentralized system. Transactions are verifiably and permanently recorded in a public ledger, aka a blockchain. (See: What Is a Blockchain?)
Most cryptos represent a unique technology with real-world applications. For example, Ethereum (ETH) is built on the idea of “smart contracts” that can be executed through its blockchain. Aave (AAVE) is using its system to securely connect borrowers and lenders without the need for a middleman. And Monero (XMR) aims to become the world’s most private, untraceable currency.
Just like stocks, every crypto has its own fundamentals, purpose and story.
How Many Cryptos Are There?
New cryptos are being developed all the time. At the start of 2021, more than 4,000 cryptos were widely available. But some sources estimate that there may be as many as 7,800 cryptocurrencies currently in existence.
That would mean that – in terms of options available – the crypto market has officially eclipsed the stock market.
What’s So Special About Bitcoin?
Everyone knows Bitcoin (BTC) because, well, it’s been around the longest. Bitcoin launched in 2009 as the first-ever decentralized digital currency. And unlike some of its more sophisticated brethren, Bitcoin simply acts as a form of digital money. That’s its sole purpose, and so…
Thanks to an easy-to-understand mission, plus Bitcoin’s first-mover advantage, it’s become the world’s most popular crypto. Whether it’s the “best” crypto or will ever be a true form of money remains up for debate… which is what makes the sector volatile and exciting.
What Was the “Bitcoin Halvening”?
Unlike fiat currencies, Bitcoin was intentionally designed with a sort of inflation “schedule.” There is a finite number of Bitcoin. And every four years (roughly), the number of new Bitcoin that can be mined gets reduced by – you guessed it – half. In 2009, 50 new Bitcoin were mined every 10 minutes. In 2011, the number dropped to 25. In 2016 it fell to 12.5. And after the last “halvening” in May 2020, the number of Bitcoin mined every 10 minutes dropped to 6.25. According to Coindesk, “This process will end with a total of 21 million coins, probably in the year 2140.” (See: What Is Crypto Mining?)
What Is an “Altcoin”?
The term “altcoin” refers to every crypto that isn’t Bitcoin. It was coined as other cryptos began to emerge in Bitcoin’s wake. In those days, every new crypto was viewed as a “Bitcoin competitor,” even if their technologies had nothing in common. And here we are still using the term, more than a decade later.
If it ain’t Bitcoin… it’s an altcoin.
What Is a “Stablecoin”?
Stablecoins are cryptos that stabilize their price by tying themselves to assets outside of cryptocurrency. Tether (USDT) is the most well-known example. It was designed to always be worth $1. There are an estimated 200 stablecoins available right now, with more on the way as nations seek to develop cryptos based on their own fiat currencies.
Which Crypto Has the Most Potential?
As we said above, every crypto has its own unique purpose. Some are used to help machines communicate. Some connect competing blockchains. And some are even seeking to solve problems that we don’t have yet, like ethical and privacy-related issues that will come with artificial intelligence (AI) adoption.
There are cryptos disrupting everything, including…
- Monetary transactions
- Transfers of medical data
- Secure electronic voting
- Supply chain monitoring
- Internet of Things (IoT) device connection.
The possibilities are endless. As such, it would be foolish to “put it all on one horse.” A smarter – and less risky – approach would be to spread your investment across multiple promising cryptos.
[If you’re interested in learning about our three favorite cryptos right now, click here.]
What Is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is an ever-growing list of records, represented as “blocks.” Every transaction creates a new block that is interlinked with the previous block and so on. The result is a permanent, decentralized public ledger that – as defined by Harvard Business Review – “can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way.”
Bitcoin’s was the first blockchain ever created. In the decade since, hundreds more have emerged, many with their own unique tweaks to Bitcoin’s original formula. There are four main types of blockchain networks:
- Public – anyone can make or view transactions (Bitcoin uses this type of blockchain).
- Private – permission is required to make or view transactions.
- Hybrid – varying combinations of public/private network features.
- Sidechain – runs parallel to another existing blockchain.
Why Are Blockchains Important?
Blockchains keep crypto users honest. By offering permanent, inalterable records of every transaction, blockchains eliminate the need for a central authority. And because the process is electronic and fully automated, users can freely exchange cryptos 24 hours a day… quickly, securely and with zero fees.
Their unprecedented safety and reliability give blockchains the potential to completely reshape the financial world. But the applications don’t stop there. Healthcare, real estate, legal contracts and supply chains are just some of the areas where blockchains are being applied right now.
What Does “DeFi” Mean?
DeFi is an abbreviation of “decentralized finance.” As we’ve covered, most cryptocurrencies are not part of any centralized system. DeFi refers to the use of blockchains as a way to disrupt traditional financial institutions.
How Do I Buy Crypto?
You can acquire crypto several ways, but the most common – and easiest – is to purchase through a crypto exchange. Crypto exchanges are to crypto what a brokerage account is to stocks. The only difference is certain cryptos are available only via certain exchanges.
Most exchanges list the cryptos available to purchase on their sites. For example, the popular exchange Coinbase lists its supported cryptos here. Kraken, another well-known exchange, lists its supported cryptos here.
Just as you would research the pros and cons of a stock brokerage before signing up, you should be sure to read reviews of any crypto exchange you’re considering.
Can I Buy Crypto in My Stock Brokerage Account?
If you’re a Robinhood user, yes. However, there are only seven cryptos currently available for trading in the Robinhood app (details here). So if you want to invest beyond the most well-known cryptos, you’re out of luck. Plus, with Robinhood, you never take full possession of your coins. You can’t go out and spend them on, say, a new Tesla.
A few traditional brokerages, including Schwab and TD Ameritrade, have made Bitcoin futures available. But at the moment, there is no way to directly invest in cryptocurrencies through the big brokerage platforms.
What’s Required to Create a Crypto Exchange Account?
The requirements vary depending on the exchange. But in most cases, creating an account is no more complicated than getting set up with a stock broker. The process for joining Coinbase, for example, looks like this:
- Verify your email address and add a mobile number for two-step verification.
- Enter personal information, like your name, date of birth, address, etc.
- Answer basic questions about your income and employment status (just as you would when signing up for any brokerage account). In some cases, you may be asked to verify your identity by snapping a picture of your ID and uploading it to your account.
- Fund your account by connecting to your preferred financial institution.
And that’s it. Most crypto exchanges list the requirements for creating an account on their website. It’s wise to get these details before you start the sign-up process. That way you can make sure to have everything handy.
Why Do Some Crypto Exchanges Not Operate in Certain States?
It has to do with states’ licensing requirements and regulations. Binance, for example, isn’t available to residents of New York, Texas and other states because it doesn’t yet have a license to operate in those places… or it doesn’t meet the states’ current requirements (which likely don’t address crypto).
Unfortunately the only way to get around this is to shop around for exchanges that are approved to operate in those states.
The good news is that these situations can largely be chalked up to growing pains. As cryptos go mainstream (the shift is already underway), the barriers to access will continue to shrink.
What’s a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet is exactly what it sounds like: A safe place for you to store your crypto until you’re ready to use it. It’s an added layer of complexity… but it creates an added layer of protection for your investment.
What Are My Crypto Wallet Options?
There are a few types of wallets you can choose from…
- Paper wallet: There are numerous sites that will generate a random QR code or a lengthy private key specific to your crypto. You can print this and store it with your other important documents. Here’s an example of what that might look like:

- Mobile wallet: A smartphone app that secures your crypto and enables you to access it on the go. Coinbase offers its own secure wallet app – helpfully labeled “Wallet.” Jaxx Liberty is another popular free option.
- “Cold” wallet: Taking your crypto completely offline and putting it on a mini hard drive or USB stick.
Each of these comes with its own pros and cons. A mobile wallet, for example, is the most convenient option for crypto traders. It grants you the ability to buy and sell quickly. Some mobile wallets will even allow you to use your crypto as a currency to pay for goods and services on the go. However… it is less secure than cold storage in the same way that the cash in your billfold is less secure than the cash in your home safe.
A paper wallet comes with caveats as well. The most glaring concern is that you’re required to upload your crypto details to a third-party website. It’s recommended that you take your computer offline while your random key is being generated, among other security measures. (There’s a solid rundown of the procedure here from bitcoinpaperwallet.) This type of wallet also may not appeal to folks who tend to store critical data on the backs of old water bills.
Do I Need a Crypto Wallet?
Yes and no. You can technically keep your crypto “on the exchange” after you buy it. That is, leave it in your exchange account as you would keep any stocks you buy in your E-Trade account. But most crypto traders don’t do this for fear of getting hacked.
(Unlike the dollars in your bank account, Bitcoin and other digital currencies are just like gold or artwork and are not FDIC-insured. So if a hacker rips you off… well, that’s between you and the police – who have a lousy track record of catching crypto thieves.)
You can always lower your risk by doing things like changing your password once a month… using two-factor authentication… downloading a password manager… etc.
But most crypto investors would rather take their coins off the exchange entirely and transfer them to a wallet.
Do I Have to Pay Taxes on My Crypto Returns?
Yes. According to the IRS, crypto gains and losses should be reported the same as you would report gains and losses associated with stocks. Here’s a blurb from the IRS:
A taxpayer generally realizes capital gain or loss on the sale or exchange of virtual currency that is a capital asset in the hands of the taxpayer. For example, stocks, bonds and other investment property are generally capital assets. A taxpayer generally realizes ordinary gain or loss on the sale or exchange of virtual currency that is not a capital asset in the hands of the taxpayer.
You can learn more – including how taxes affect crypto miners and crypto received as a gift – on the IRS website here.
Coinbase also offers a helpful crypto tax FAQ here.
What Are the Risks Involved in Buying and Selling Crypto?
Despite the fact that cryptocurrencies have been around for more than a decade, they are still an emerging asset. So beyond the usual risk posed by any investment, be it stocks, bonds or options (i.e., losing money), cryptos are vulnerable to the whims of lawmakers and regulatory bodies.
But with that said… we may have already reached the tipping point for crypto. Consider this…
- A flurry of investment recently pushed the market cap for all cryptos above $1 trillion…
- Bitcoin is being bought up by pension fund managers, insurance companies and corporate treasurers…
- Several major payment processors now offer digital currency transactions…
- And JPMorgan Chase, the world’s most valuable bank, has hopped on the bandwagon and developed its own cryptocurrency called JPM Coin (JPM).
Just look at how crypto exchange volume exploded in 2020:
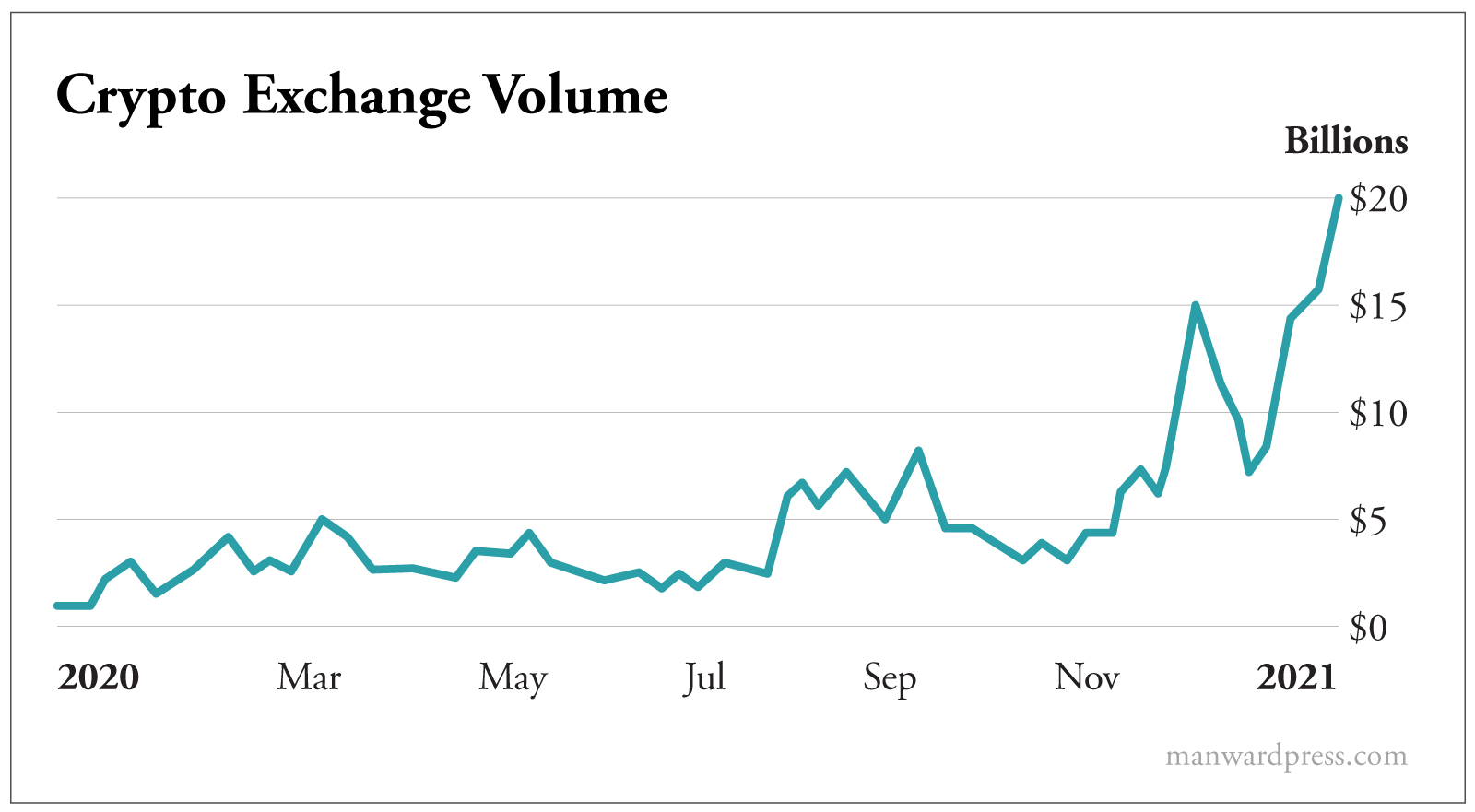
Cryptos are going mainstream. And as they do, it will only get harder for regulators to put the lid back on the jar.
None of that is to say you shouldn’t take every precautionary step before you invest in crypto. The same simple rules that you apply to stocks should be applied here: Do your research… have an exit plan… and NEVER put in more money than you can afford to lose.
Why Are Some Cryptos So Volatile?
Crypto trading volume has increased exponentially… but it’s still nowhere near what you’d see in midcap or even small cap stocks. With prices low and volume thin, even a modest surge in interest can send crypto prices soaring. And on the flip side… when investors suddenly pull out of a crypto, prices can quickly deflate.
It’s the type of action that should be quite familiar to penny stock traders. Fortunately, as we’ve seen, that increased risk comes with tremendous upside.
I’m Ready to Get Started With Crypto! What Now?
Your timing is perfect. Crypto had a record year in 2020. But our research shows that it was all a mere preview of what’s to come…
We’re convinced that the best way capitalize on this once-in-a-generation opportunity isn’t through Bitcoin, Ethereum or any well-known crypto…
It’s through the “penny stocks” of the crypto world…
Crypto 201
In the simplest possible terms… crypto “mining” is the process of verifying transactions on the blockchain. (Crypto miners essentially act as blockchain auditors.) To do this, tech-savvy folks around the globe use high-powered computers to solve the same complex equations. Each equation represents a transaction, and when enough users reach the same solution, the transaction is officially verified and recorded. Crypto miners are rewarded for their time – and processing power – with free crypto.
Crypto mining is important for two reasons. First, it keeps the blockchain honest. But more importantly, it releases new crypto into existence. Without Bitcoin miners, for example, no new Bitcoin would be released… ever.
Sound complex? It is. And there’s a whole lot more to it. Fortunately, most crypto investors purchase through an exchange. It’s the quickest and easiest way to get started… no mining required.
How Does “Yield Farming” Work?
Similar to crypto mining, yield farming allows holders of certain cryptos to participate in transaction validation – aka “staking” – in exchange for more crypto. It’s a way to juice your returns by contributing to the network.
Per Cointelegraph, “The general idea is that individuals can earn tokens in exchange for their participation in DeFi applications… As each new project that emerges offers new tokens or ways to earn rewards, users have been flocking to it, hoping to get a cut of the yield on offer. In turn, this creates a demand that pushes up the value invested in the project and the tokens.”



